Understanding Edge Computing
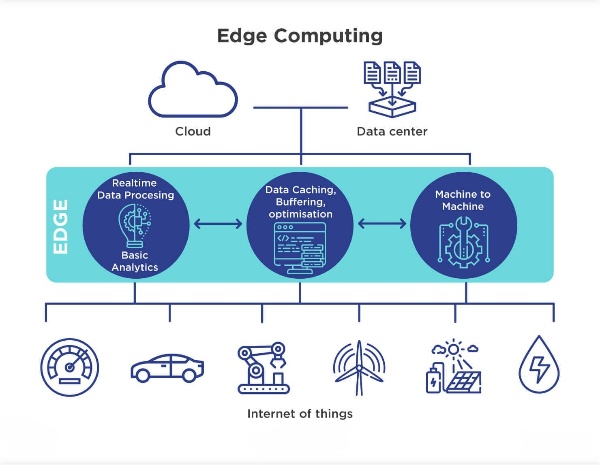
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that processes data near the data source or at the network’s edge, rather than relying on a centralized cloud server. This model reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, and improves real-time processing capabilities. Edge devices, which include sensors, IoT devices, and gateways, perform data processing tasks locally, sending only the relevant data to the cloud for further analysis or storage.
This decentralized approach contrasts with traditional cloud computing, where data is sent to a centralized server, often located far from the data source. By processing data at the edge, organizations can achieve faster response times, enhance security, and reduce the strain on their cloud infrastructure.
The Synergy Between Edge and Cloud Computing
While edge computing offers significant advantages, it is not a replacement for cloud computing. Instead, the two technologies work in synergy to create a more efficient and responsive computing environment. Edge computing handles time-sensitive data and processes it locally, reducing the need for constant communication with the cloud. This approach not only reduces latency but also minimizes the amount of data transmitted to the cloud, thus conserving bandwidth.
Cloud computing, on the other hand, excels in handling large-scale data processing, storage, and analytics. It provides the computational power and scalability needed to analyze vast amounts of data, apply machine learning models, and generate insights that drive business decisions. When combined with edge computing, cloud services become more effective, as they can focus on processing and analyzing the most relevant data, rather than being overwhelmed by raw data from numerous edge devices.
Benefits of Integrating Edge Computing with Cloud Services
Reduced Latency and Improved Response Times: Edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, ensuring faster response times. This is crucial for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring.
Bandwidth Optimization: Edge computing optimizes bandwidth by reducing the data sent to the cloud. It processes data locally and sends only relevant information, minimizing network load. This is essential in bandwidth-limited or expensive scenarios.
Enhanced Security and Privacy: Processing data at the edge enhances security and privacy by keeping sensitive information close to its source. This approach reduces the risk of data breaches during cloud transmission. It allows for stronger local security measures, crucial in industries like healthcare and finance.
Scalability and Flexibility: Edge computing combined with cloud services offers scalability and flexibility. Organizations can deploy edge devices as needed, adapting quickly to changing demands. This approach eliminates concerns about cloud infrastructure limitations, allowing efficient scaling of operations.
Cost Efficiency: Edge computing reduces costs by offloading data processing to edge devices, decreasing reliance on cloud services. It also cuts expenses related to data transmission and storage, further improving cost efficiency.
Challenges of Edge Computing in Cloud Services
While the integration of edge computing with cloud services offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that organizations must address to fully realize its potential.
Complexity in Deployment and Management: Managing a distributed network of edge devices is complex and resource-intensive. Organizations must configure, maintain, and update their edge devices properly. Robust management tools and strategies are essential to handle the increased complexity of decentralized computing.
Interoperability Issues: Edge computing involves diverse devices, platforms, and protocols, leading to interoperability challenges. Ensuring seamless communication between edge devices and cloud services is critical. Organizations must invest in standardized protocols and platforms to facilitate interoperability and avoid vendor lock-in.
Data Security Concerns: Edge computing enhances security by keeping data closer to its source, but it introduces new risks. Edge devices face vulnerabilities like physical tampering, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access. Organizations must implement strong security measures to protect their edge infrastructure and ensure data integrity.
Resource Constraints: Edge devices have limited computational power, storage, and energy resources compared to centralized cloud servers. This limitation affects the types of applications run at the edge. Careful optimization is necessary to use resources efficiently and balance the computational load between edge devices and the cloud, maintaining performance.
The integration of edge computing with cloud services has opened up new possibilities across various industries. Here are some key use cases where this combination is making a significant impact: Industrial IoT (IIoT): In manufacturing and industrial sectors, edge computing monitors equipment and optimizes operations in real-time. Processing data at the edge helps manufacturers reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and enhance safety. Cloud services then analyze aggregated data for long-term insights and strategic decisions. Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles rely on real-time data to navigate and make decisions. Edge computing processes this data locally, reducing latency and ensuring quick responses. The cloud stores and analyzes data from multiple vehicles, enabling continuous learning and improvement of autonomous systems. Smart Cities: Smart cities use edge computing to manage data from sensors, cameras, and other devices throughout the city. This allows real-time monitoring of traffic, energy usage, and public safety. Cloud services aggregate and analyze data from multiple sources, helping city planners improve infrastructure and services. Healthcare: In healthcare, edge computing monitors patients in real-time, allowing quick responses to emergencies. Wearable devices and IoT sensors process data locally, ensuring patient privacy and reducing data transmission needs. The cloud stores and analyzes patient data over time, supporting long-term care and research. Retail: Retailers use edge computing to enhance the customer experience with personalized services and improved inventory management. Edge devices process data from in-store sensors and cameras. Retailers can then optimize store layouts, manage stock levels, and offer personalized promotions. Cloud services analyze customer behavior and preferences, driving targeted marketing and sales strategies.Use Cases of Edge Computing in Cloud Services
The Future of Edge and Cloud Computing
As edge computing adoption grows, the impact of edge computing on cloud services will become even more significant. The future of computing lies in integrating edge and cloud technologies seamlessly. This integration creates a hybrid model that leverages the strengths of both technologies.
One key trend is the development of multi-access edge computing (MEC). MEC aims to bring cloud capabilities to the network edge. It will enable advanced applications like augmented reality, virtual reality, and 5G-enabled services. This will spur innovation in gaming, entertainment, and telecommunications.
Another trend is the rise of edge-native applications. These applications are designed specifically for edge environments. They fully utilize low latency, real-time processing, and localized data storage offered by edge computing. As these applications mature, they will increase demand for advanced edge infrastructure and services.
The impact of edge computing on cloud services is also shaped by AI and machine learning. AI-powered edge devices make intelligent decisions locally. This reduces the need for constant cloud communication. Consequently, systems across various industries will become more autonomous and efficient, from smart homes to autonomous vehicles.
To fully realize the impact of edge computing on cloud services, organizations must tackle challenges related to deployment, management, security, and interoperability. As edge and cloud technologies evolve, businesses need a strategic approach. This approach should leverage both technologies’ strengths to ensure a robust, scalable, and efficient computing environment.
Conclusion
Edge computing is revolutionizing the way data is processed and managed, offering significant advantages in terms of latency, bandwidth optimization, security, and scalability. When combined with cloud services, it creates a powerful computing model that is well-suited to meet the demands of modern applications and industries. While challenges exist, the continued development of edge computing technologies and their integration with cloud services will drive innovation and create new opportunities for businesses across the globe.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, organizations must embrace the synergy between edge and cloud computing to remain competitive and agile. By doing so, they can unlock the full potential of their data, improve operational efficiency, and deliver better outcomes for their customers.
Author:Golvez Technology
